PEFT in HuggingFace Libraries#
PEFT methods are seamlessly integrated with 🤗 Accelerate, supporting large-scale models through DeepSpeed and Big Model Inference.
Supported PEFT Methods#
LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation for efficient model adaptation. Paper
Prefix Tuning: Optimizes continuous prompts for generation tasks. Paper1, Paper2
P-Tuning: Utilizes prompts for understanding model behavior. Paper
Prompt Tuning: Harnesses the power of scale for parameter-efficient prompt tuning. Paper
AdaLoRA: Adaptive Budget Allocation for fine-tuning. Paper
\((IA)^3\): Enhances fine-tuning effectiveness and efficiency. Paper
MultiTask Prompt Tuning: Enables transfer learning across multiple tasks. Paper
LoHa: Combines Low-Rank and Hadamard Product for efficient learning. Paper
LoKr: Incorporates Kronecker Adapter for tuning. Paper
Getting Started with PEFT#
Here’s a Python snippet demonstrating how to use LoRA with a sequence-to-sequence model:
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
from peft import get_peft_config, get_peft_model, LoraConfig, TaskType
model_name_or_path = "bigscience/mt0-large"
tokenizer_name_or_path = "bigscience/mt0-large"
peft_config = LoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1
)
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
model.print_trainable_parameters()
# output: trainable params: 2359296 || all params: 1231940608 || trainable%: 0.19151053100118282
Use Cases#
Get comparable performance to full finetuning by adapting LLMs to downstream tasks using consumer hardware#
GPU memory required for adapting LLMs on the few-shot dataset ought/raft/twitter_complaints. Here, settings considered
are full finetuning, PEFT-LoRA using plain PyTorch and PEFT-LoRA using DeepSpeed with CPU Offloading.
Hardware: Single A100 80GB GPU with CPU RAM above 64GB
Model |
Full Finetuning |
PEFT-LoRA PyTorch |
PEFT-LoRA DeepSpeed with CPU Offloading |
|---|---|---|---|
bigscience/T0_3B (3B params) |
47.14GB GPU / 2.96GB CPU |
14.4GB GPU / 2.96GB CPU |
9.8GB GPU / 17.8GB CPU |
bigscience/mt0-xxl (12B params) |
OOM GPU |
56GB GPU / 3GB CPU |
22GB GPU / 52GB CPU |
bigscience/bloomz-7b1 (7B params) |
OOM GPU |
32GB GPU / 3.8GB CPU |
18.1GB GPU / 35GB CPU |
Performance of PEFT-LoRA tuned bigscience/T0_3B on ought/raft/twitter_complaints leaderboard.
A point to note is that we didn’t try to squeeze performance by playing around with input instruction templates, LoRA hyperparams and other training related hyperparams. Also, we didn’t use the larger 13B mt0-xxl model.
So, we are already seeing comparable performance to SoTA with parameter efficient tuning. Also, the final additional checkpoint size is just 19MB in comparison to 11GB size of the backbone bigscience/T0_3B model, but one still has to load the original full size model.
Submission Name |
Accuracy |
|---|---|
Human baseline (crowdsourced) |
0.897 |
Flan-T5 |
0.892 |
lora-t0-3b |
0.863 |
Therefore, we can see that performance comparable to SoTA is achievable by PEFT methods with consumer hardware such as 16GB and 24GB GPUs.
An insightful blogpost explaining the advantages of using PEFT for fine-tuning FlanT5-XXL: https://www.philschmid.de/fine-tune-flan-t5-peft
Parameter Efficient Tuning of Diffusion Models#
GPU memory required by different settings during training is given below. The final checkpoint size is 8.8 MB.
Hardware: Single A100 80GB GPU with CPU RAM above 64GB
Model |
Full Finetuning |
PEFT-LoRA |
PEFT-LoRA with Gradient Checkpointing |
|---|---|---|---|
CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 |
27.5GB GPU / 3.97GB CPU |
15.5GB GPU / 3.84GB CPU |
8.12GB GPU / 3.77GB CPU |
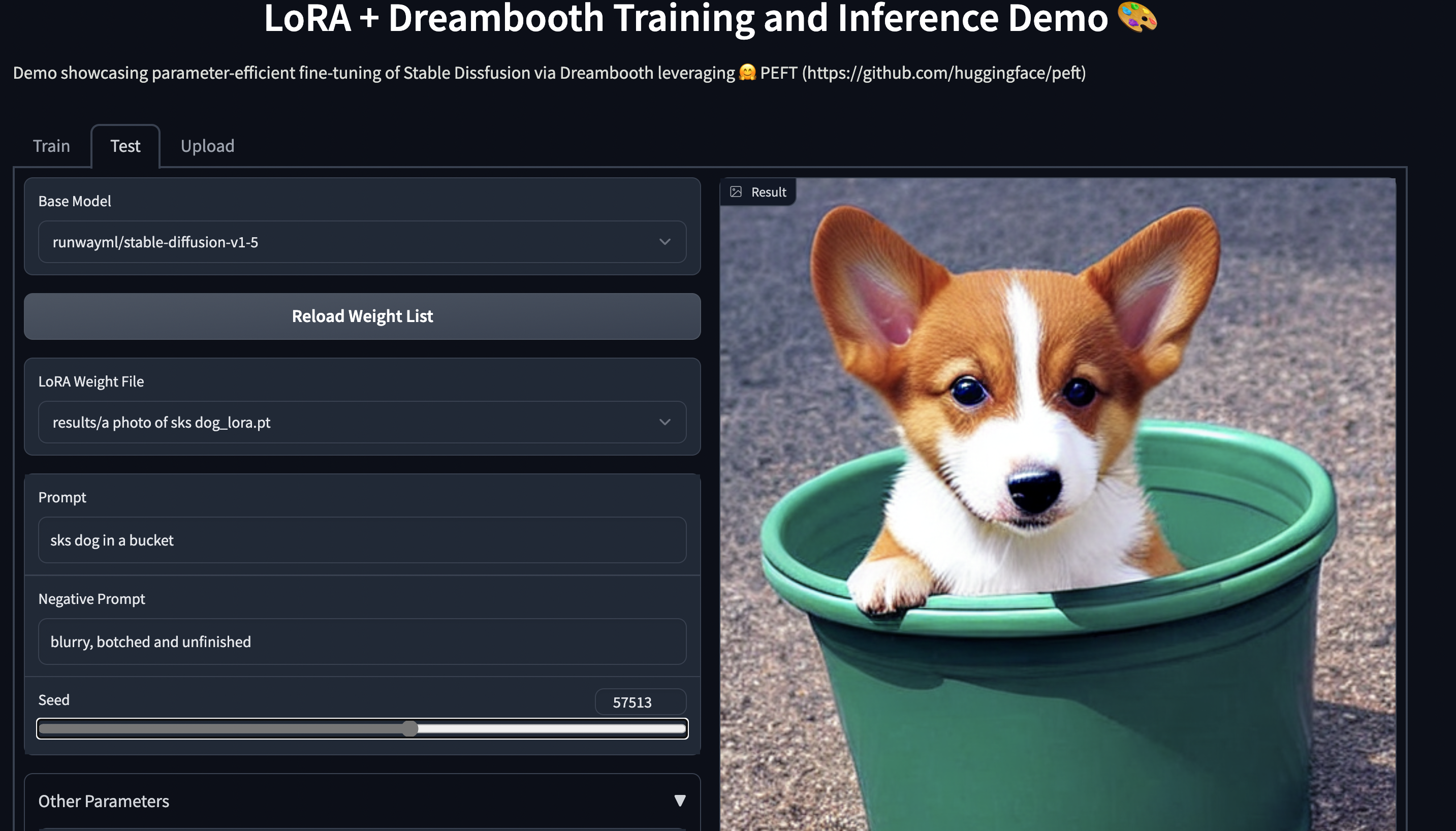
Training
An example of using LoRA for parameter efficient dreambooth training is given in examples/lora_dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py
export MODEL_NAME= "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4" #"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1"
export INSTANCE_DIR="path-to-instance-images"
export CLASS_DIR="path-to-class-images"
export OUTPUT_DIR="path-to-save-model"
accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
--class_data_dir=$CLASS_DIR \
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
--train_text_encoder \
--with_prior_preservation --prior_loss_weight=1.0 \
--instance_prompt="a photo of sks dog" \
--class_prompt="a photo of dog" \
--resolution=512 \
--train_batch_size=1 \
--lr_scheduler="constant" \
--lr_warmup_steps=0 \
--num_class_images=200 \
--use_lora \
--lora_r 16 \
--lora_alpha 27 \
--lora_text_encoder_r 16 \
--lora_text_encoder_alpha 17 \
--learning_rate=1e-4 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps=1 \
--gradient_checkpointing \
--max_train_steps=800
Try out the 🤗 Gradio Space which should run seamlessly on a T4 instance: smangrul/peft-lora-sd-dreambooth.
NEW ✨ Multi Adapter support and combining multiple LoRA adapters in a weighted combination

NEW ✨ Dreambooth training for Stable Diffusion using LoHa and LoKr adapters examples/stable_diffusion/train_dreambooth.py
Parameter Efficient Tuning of LLMs for RLHF components such as Ranker and Policy#
Here is an example in trl library using PEFT+INT8 for tuning policy model: gpt2-sentiment_peft.py and corresponding Blog
Example using PEFT for Instruction finetuning, reward model and policy : stack_llama and corresponding Blog
INT8 training of large models in Colab using PEFT LoRA and bits_and_bytes#
Here is now a demo on how to fine tune OPT-6.7b (14GB in fp16) in a Google Colab:
Here is now a demo on how to fine tune whisper-large (1.5B params) (14GB in fp16) in a Google Colab:
and
Save compute and storage even for medium and small models#
Save storage by avoiding full finetuning of models on each of the downstream tasks/datasets,
With PEFT methods, users only need to store tiny checkpoints in the order of MBs all the while retaining
performance comparable to full finetuning.
An example of using LoRA for the task of adapting LayoutLMForTokenClassification on FUNSD dataset is given in ~examples/token_classification/PEFT_LoRA_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.py. We can observe that with only 0.62 % of parameters being trainable, we achieve performance (F1 0.777) comparable to full finetuning (F1 0.786) (without any hyperparam tuning runs for extracting more performance), and the checkpoint of this is only 2.8MB. Now, if there are N such datasets, just have these PEFT models one for each dataset and save a lot of storage without having to worry about the problem of catastrophic forgetting or overfitting of backbone/base model.
Another example is fine-tuning roberta-large on MRPC GLUE dataset using different PEFT methods. The notebooks are given in ~examples/sequence_classification.
PEFT + 🤗 Accelerate#
PEFT models work with 🤗 Accelerate out of the box. Use 🤗 Accelerate for Distributed training on various hardware such as GPUs, Apple Silicon devices, etc during training. Use 🤗 Accelerate for inferencing on consumer hardware with small resources.
Example of PEFT model training using 🤗 Accelerate’s DeepSpeed integration#
DeepSpeed version required v0.8.0. An example is provided in ~examples/conditional_generation/peft_lora_seq2seq_accelerate_ds_zero3_offload.py.
a. First, run accelerate config --config_file ds_zero3_cpu.yaml and answer the questionnaire.
Below are the contents of the config file.
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
deepspeed_config:
gradient_accumulation_steps: 1
gradient_clipping: 1.0
offload_optimizer_device: cpu
offload_param_device: cpu
zero3_init_flag: true
zero3_save_16bit_model: true
zero_stage: 3
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
downcast_bf16: "no"
dynamo_backend: "NO"
fsdp_config: {}
machine_rank: 0
main_training_function: main
megatron_lm_config: {}
mixed_precision: "no"
num_machines: 1
num_processes: 1
rdzv_backend: static
same_network: true
use_cpu: false
b. run the below command to launch the example script
accelerate launch --config_file ds_zero3_cpu.yaml examples/peft_lora_seq2seq_accelerate_ds_zero3_offload.py
c. output logs:
GPU Memory before entering the train : 1916
GPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): 66
GPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): 7488
GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): 9404
CPU Memory before entering the train : 19411
CPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): 0
CPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): 0
CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): 19411
epoch=4: train_ppl=tensor(1.0705, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0681, device='cuda:0')
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 7/7 [00:27<00:00, 3.92s/it]
GPU Memory before entering the eval : 1982
GPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): -66
GPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): 672
GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): 2654
CPU Memory before entering the eval : 19411
CPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): 0
CPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): 0
CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): 19411
accuracy=100.0
eval_preds[:10]=['no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint']
dataset['train'][label_column][:10]=['no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint']
Example of PEFT model inference using 🤗 Accelerate’s Big Model Inferencing capabilities#
An example is provided in ~examples/causal_language_modeling/peft_lora_clm_accelerate_big_model_inference.ipynb.
Conclusion#
The compatibility of PEFT with tools like 🤗 Accelerate and DeepSpeed illustrates its practicality and adaptability in real-world applications. This compatibility ensures that PEFT can be easily integrated into existing workflows, allowing for seamless scaling and adaptation of models.