LLM App Ecosystem#
This lecture dissects the emerging ecosystem for developing applications with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides an overview of the LLM stack, as illustrated by the venture capital firm Andreessen-Horowitz, with a particular focus on the data layer, orchestration frameworks, and operational tools. The session outlines how conventional developer tools are evolving to fit into this new AI-centric landscape and compares this ecosystem to its predecessors. Lastly, it examines how this new ecosystem acts as a bridge from traditional cloud development to an AI-based developer environment.
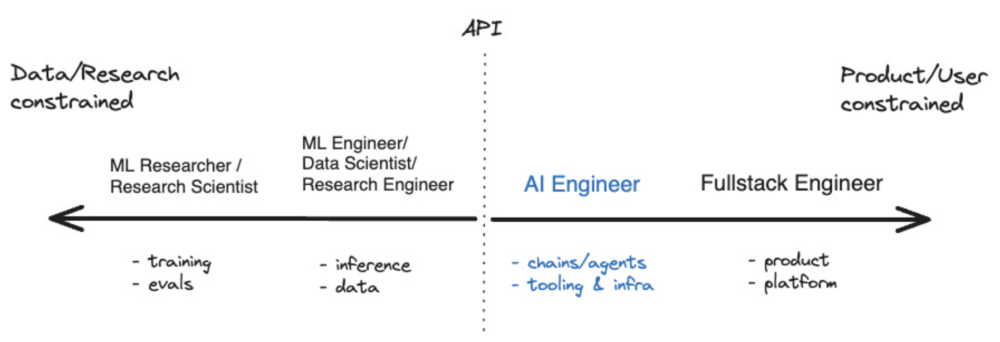
Introduction#
As AI engineering matures, the developer landscape is experiencing an exciting transition: the rise of AI engineers specialized in Large Language Models (LLMs). Firms like Andreessen-Horowitz have delineated what an LLM application stack looks like, highlighting the convergence of data engineering, orchestration, and operational capabilities required for leveraging these powerful models.
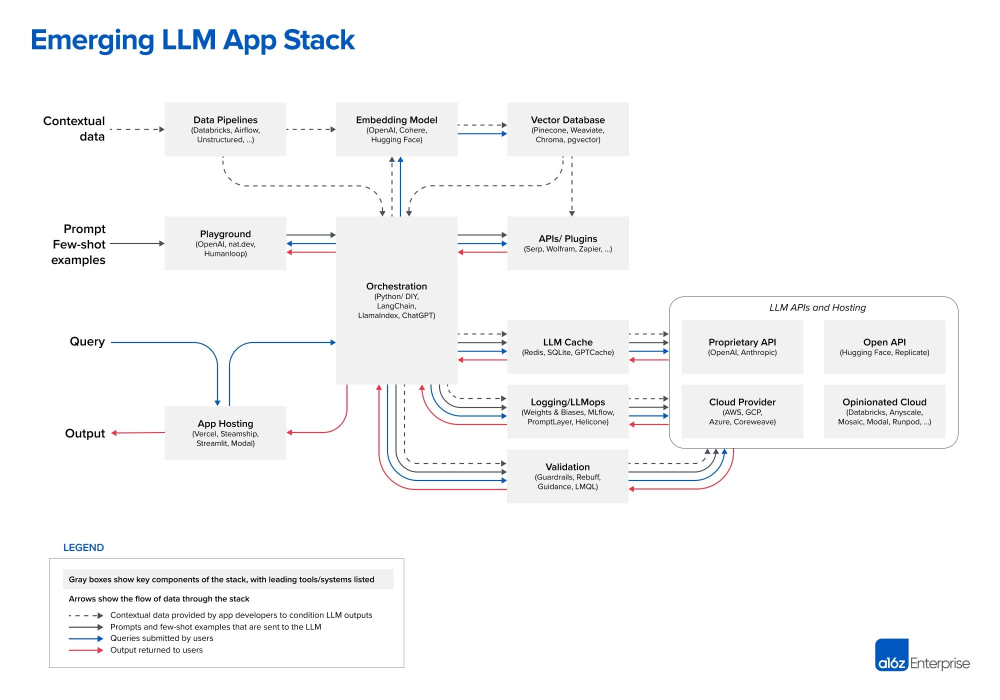
The All-Important Data Layer#
At the top layer of the LLM stack is data, which can be divided into three sub-components:
Data Pipeline: Tools like Databricks and Airflow, or even unstructured approaches, are essential for data ingestion.
Data Intelligence: These are tools that help in data curation and cleansing, exemplified by companies like Alation.
Vector Database: This is the storage mechanism for high-dimensional vectors, often used in combination with data pipeline tools.
Prompts and Queries#
This layer deals with the direct interaction between applications and the LLM. Orchestration frameworks such as LangChain and LlamaIndex simplify the complexities of prompt chaining, API interfacing, and maintaining memory across multiple LLM calls.
LLM Ops#
This operational layer contains services like LLM caching and validation. It also incorporates existing cloud and API services, extending the ecosystem into something familiar to any developer versed in DevOps. Companies like Harness have begun incorporating AI capabilities to streamline the CI/CD process, thus blurring the lines between traditional DevOps and MLOps.
Playground Tools#
This intriguing category consists of platforms like Humanloop that provide an environment for experimenting with various prompting techniques and their real-world application.
AI’s Evolutionary Role in Development#
AI is fundamentally changing the paradigm of developer productivity by automating tedious tasks, enabling focus on high-impact work. As the AI era emerges, tools from the cloud-native era are being adapted to serve the needs of AI engineers.
Concluding Remarks#
The LLM app stack represents not just an evolution but a synthesis of technologies, from data engineering to DevOps, all centered around the capabilities of Large Language Models. It creates a bridge between conventional cloud development practices and the next wave of AI-centric development.