Requirements Engineering (RE)#
This lecture note aims to provide an in-depth overview of Requirements Engineering (RE), a cornerstone in the engineering design process. The discussion covers the five critical steps in the RE process: Feasibility Study, Requirement Elicitation and Analysis, Software Requirement Specification, Software Requirement Validation, and Software Requirement Management. Types of feasibility, problems in elicitation and analysis, models used for specification, and categories of software requirements are elaborated.
Requirement Engineering Process#
Requirements Engineering (RE) serves as a foundational stage in software development, providing mechanisms to clearly understand, document, and manage what a customer desires in a proposed system.
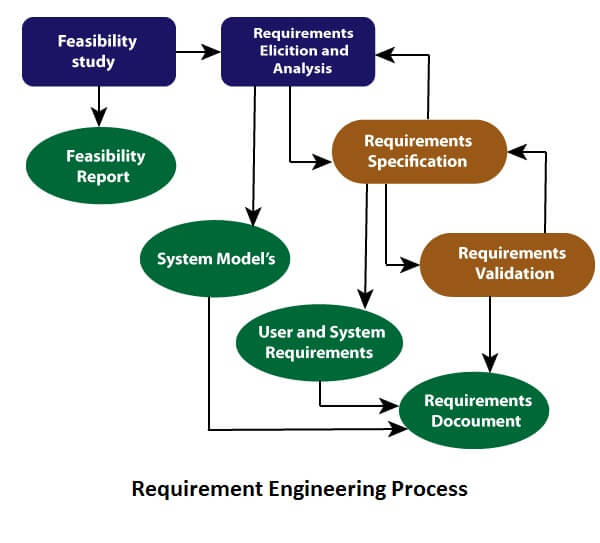
1. Feasibility Study#
Objective: To justify the development of the software that meets user needs, adheres to change, and complies with standards.
Types of Feasibility:
Technical Feasibility: Evaluates if current technologies can meet customer requirements.
Operational Feasibility: Measures how well the software solves business problems and meets customer requirements.
Economic Feasibility: Assesses the software’s financial viability.
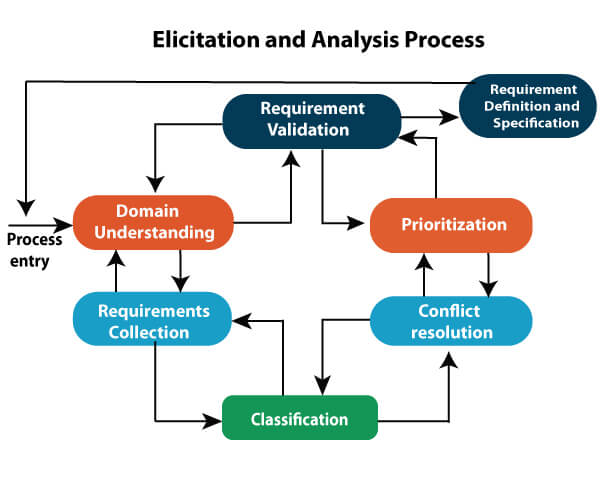
2. Requirement Elicitation and Analysis#
Gathering Requirements: Involves consultations with customers and reviewing existing system processes.
Challenges in Elicitation and Analysis:
Involving the right stakeholders
Resolving conflicting requirements
Addressing stakeholder ambiguity and indecision
3. Software Requirement Specification (SRS)#
Models Used: Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ER), Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs), Data Dictionaries, Function Decomposition Diagrams (FDDs)
Document Creation: Transforms customer needs into technical language for the development team.
4. Software Requirement Validation#
Validation Techniques:
Requirements reviews/inspections
Prototyping
Test-case generation
Automated consistency analysis
5. Software Requirement Management#
Change Management: Handling evolving requirements and shifting priorities.
Prerequisites: Requirements must be clear, correct, consistent, and more.
Categories of Software Requirements#
Functional Requirements: Describe what the system should do.
Non-Functional Requirements: Specify quality attributes like security, usability, maintainability.
Non-Functional Requirements Categories:#
Execution Qualities: Security, Usability
Evolution Qualities: Testability, Maintainability
Summary#
A comprehensive understanding of Requirements Engineering provides the groundwork for successful software development. However, it is not devoid of challenges such as stakeholder conflicts and shifting requirements. Alternative methodologies such as Agile or Lean could be used to facilitate a more adaptive approach to requirements engineering.
The utilization of advanced analytics tools and Natural Language Processing (NLP) could also enhance the effectiveness of requirements gathering and validation. These tools can automatically analyze customer conversations and documents to extract crucial requirements, thereby improving efficiency and accuracy.