Text Data Collection#
In natural language processing and computational linguistics, the foundation of any language model is the corpus. A corpus, or corpora in plural, is a collection of language samples, gathered for specific research purposes. The development of computers has made it easier to analyze corpora, and for improved accuracy, it is common to perform morphological analysis on the natural language samples. The use of probabilistic and statistical techniques, combined with a chronological approach, allows for a comprehensive understanding of the corpus. It serves as essential material for modern linguistic research and can be considered a successful application of scientific methodology in humanities.
Corpora Sources#
Several sources provide access to different types of corpora. Some of the popular sources include:
National Institute of Korean Language’s Everyone’s Corpus#
This source provides a systematic collection of various analysis corpora (such as morphological and syntactic analysis corpora), corpora from different domains (written, newspapers, spoken, web), and corpora for natural language inference (similar sentences). Users need to log in, verify their email, and provide information about their research project and the duration of the agreement to access and download the data.

Fig. 34 National Institute of Korean Language’s Everyone’s Corpus#
AIHub#
AIHub offers a wide range of data, from text to speech and multimodal data. Users can access the data by logging in, specifying the purpose and duration of use, and submitting an application. Once the request is approved, users receive an email granting access to the data.
Fig. 35 AIHub#
The eKorpkit Corpus#
The eKorpkit Corpus is a large, diverse, and multilingual (Korean and English) dataset for language modeling. The total size of the dataset is 448.87 GiB, with 258.83 GiB in English and 190.04 GiB in Korean.
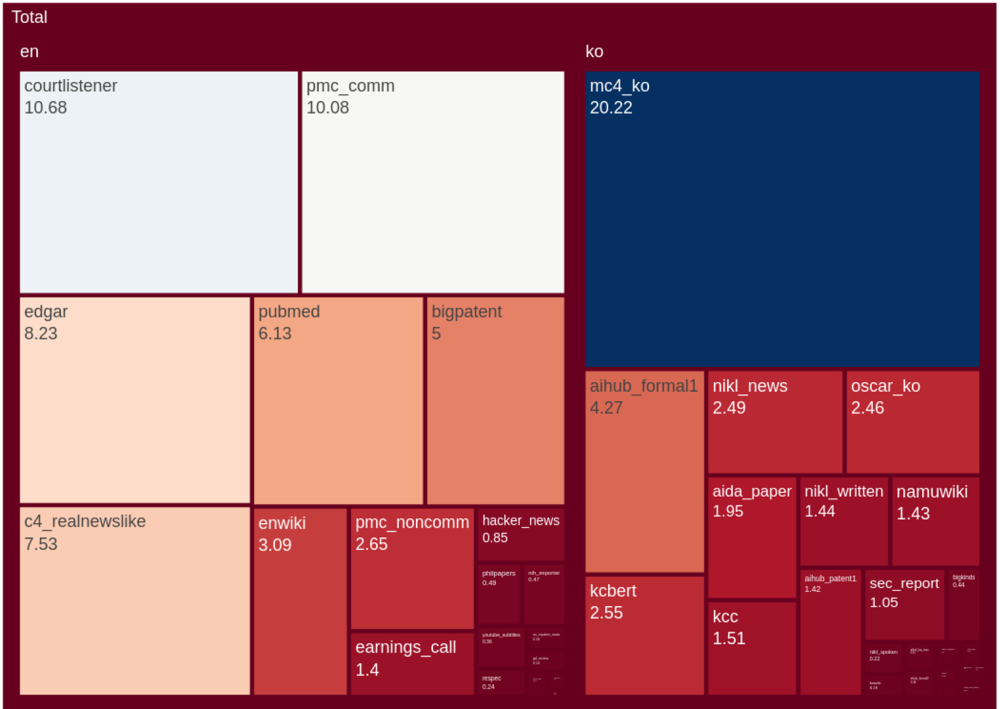
Fig. 36 The eKorpkit Corpus#
Text Data Collection Overview#
Text data can be collected from various sources such as web pages, social media platforms, comments, audio, video, and any other source that can be converted into a text format. The data can be stored in various formats, including plain text, PDF, tables, XML, and JSON. Collection methods include web crawling, API calls, database queries, and online surveys.

Fig. 37 Text Data Collection#
Text Data Collection Types#
Offline Data#
Offline data can be collected through on-site or offline surveys, audio recordings, or video recordings. This method allows for targeted data collection but requires manual effort and is subject to temporal and spatial constraints.
Internal System Data#
Data can also be collected from internal systems such as company databases, internal message boards, user comments, business reports, and internal documents. This method allows for quick access to existing data but may be restricted to affiliated organizations or services and carries a risk of information leakage.
Web Crawling#
Web crawling involves using programming languages to repeatedly collect large amounts of information from web pages. This method enables rapid and large-scale data collection and can also help in creating a normalized dataset. However, it requires proficiency in programming languages and may be susceptible to privacy issues.
API Calls#
API calls can be used to collect data officially provided by a service. Examples of APIs include Naver API, Kakao API, Reddit API, News API, and social media platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram. This method allows access to high-quality data, but the available sources may be limited, and programming language skills are necessary.
Data Dumps#
Some websites offer data dumps, which are downloadable files containing a snapshot of the website’s database. Examples include:
Namoo Wiki: Namoo Wiki provides database dump files to prevent server overload from web crawling. These files are intended for big data analysis, mirror creation, or personal collection purposes.
Wikipedia: Wikipedia regularly releases bundled archives of all its articles for users with various purposes, such as data analysis or offline access.
NCBI: The majority of NCBI data are available for download, either directly from the NCBI FTP site or by using software tools to download custom datasets.
Common Crawl#
Common Crawl is a non-profit organization that crawls the web and freely provides archives and datasets to the public. The Common Crawl web archive consists of petabytes of data collected since 2011, with new data added every month. Founded by Gil Elbaz, the organization’s crawler adheres to nofollow and robots.txt policies, and open-source code for processing the Common Crawl datasets is publicly available. In 2012, Amazon Web Services began hosting the Common Crawl archive through its Public Dataset Program. The organization releases .arc files, metadata files, and the crawler’s text output. Common Crawl data has been used to train OpenAI’s GPT-3 language model.
Web Crawling#
Web crawling is the process of extracting information from web pages. It involves navigating through the internet by following hyperlinks and downloading web pages to obtain the necessary data. Web crawling is an essential technique for collecting data from websites and is widely used in various applications, such as search engines, data analysis, and content aggregation.
Static vs. Dynamic Web Pages#
There are two types of web pages: static and dynamic.
Static web pages are those that display the same content to every user without any variation. These pages are pre-built and stored on the server as HTML and CSS files. When a user requests a static page, the server sends the corresponding HTML and CSS files to the user’s browser. Static web pages are fast and put less strain on the server but can be difficult to update or modify.
Dynamic web pages, on the other hand, can display different content based on various factors, such as user input or time. These pages are generated on-the-fly by the server using server-side scripting languages like PHP or JavaScript. Dynamic web pages offer more flexibility and customization but can be more complex to manage and may be less secure.
Web Crawling vs. Web Scraping#
While the terms web crawling and web scraping are often used interchangeably, they refer to distinct processes:
Web Crawling: Involves downloading web pages by following hyperlinks and extracting data from them. Web crawling is typically performed by automated bots or spiders that systematically traverse the internet.
Web Scraping: Refers to the process of extracting specific information from a downloaded web page. Web scraping can be thought of as a more targeted approach to data extraction, focusing on specific elements within a web page.
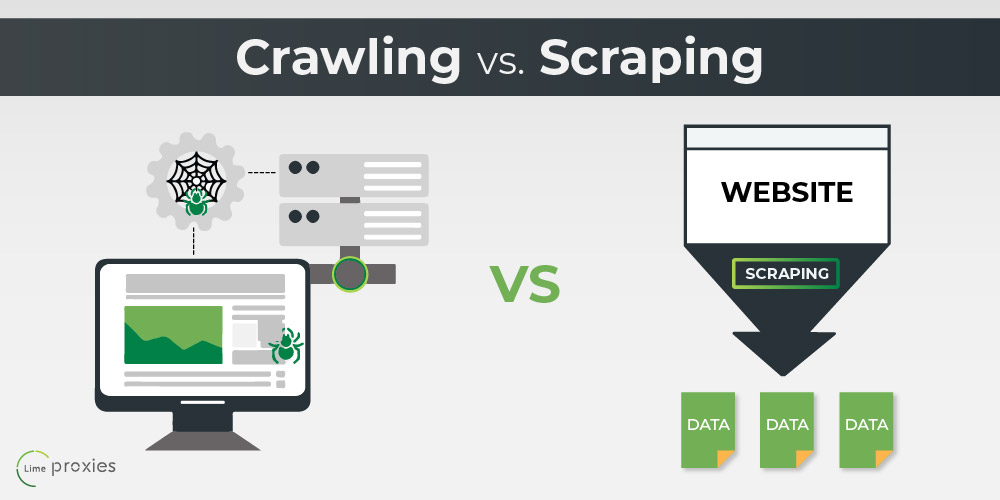
Fig. 38 Web Crawling vs. Web Scraping#
Legal Issues in Web Crawling#
Web crawling may raise legal concerns, particularly when it comes to unauthorized data collection and copyright infringement. To mitigate these risks, crawlers should adhere to the guidelines specified in the robots.txt file, which is a text file placed on a website to inform crawlers about which parts of the site can be accessed and scraped. It is essential to obtain permission from the website owner if the robots.txt file is not available or if it does not explicitly allow data collection.
Static and Dynamic Data Collection#
Different Python packages are used for collecting data from static and dynamic web pages.
Static Data Collection |
Dynamic Data Collection |
|
|---|---|---|
Python Packages |
requests / urllib |
selenium |
Coverage |
Static web pages |
Static and dynamic web pages |
Speed |
Fast (no page manipulation) |
Relatively slow |
Parsing Package |
BeautifulSoup |
BeautifulSoup / selenium |
Static data collection involves downloading the HTML content of static web pages using the requests or urllib Python packages. The HTML content is then parsed using BeautifulSoup to extract the desired information. This method is fast as it directly fetches the URL’s HTML content. However, it may not be suitable for all types of web pages.
Dynamic data collection involves interacting with dynamic web pages using the selenium Python package to control a web browser, such as ChromeDriver. This method allows for more complex interactions, such as logging in, clicking buttons, or navigating to specific pages. Dynamic data collection is more versatile than static data collection but can be slower as it involves browser manipulation and waiting for the browser to load content.