Introduction to MLOps#
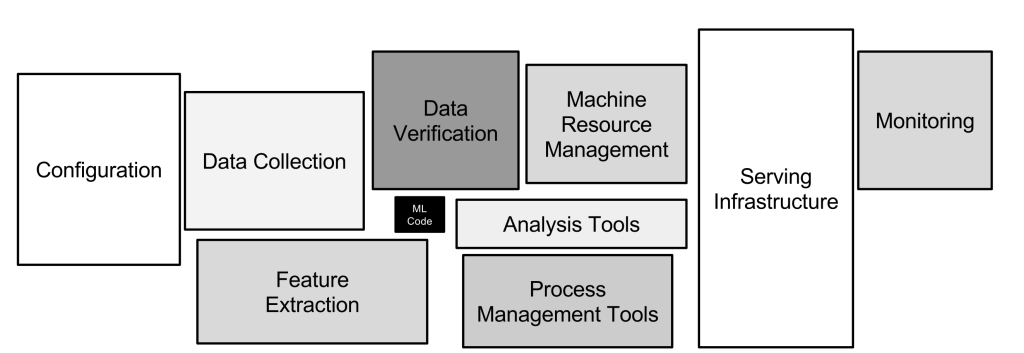
Machine learning systems design is the process of creating and implementing machine learning models and algorithms that can solve real-world problems. This involves defining the software architecture, selecting the appropriate algorithms, and designing the infrastructure required for the system to meet specific requirements.
The design process typically involves several stages, such as collecting and preparing data, selecting relevant features, training and validating the model, and integrating it into the broader system or application. Additionally, monitoring and maintenance are essential to ensure that the machine learning system continues to perform accurately and efficiently over time.
MLOps, or Machine Learning Operations, is a related field that applies DevOps principles to machine learning systems. MLOps focuses on developing a software architecture that can handle the complexity and scalability of machine learning models, managing data, and infrastructure required for training and deploying models, and automating processes to improve efficiency and reliability.
Machine learning systems design and MLOps are critical to ensuring the success of machine learning projects, improving the accuracy and efficiency of models, and delivering value to users and customers.
In summary, this chapter covers the following topics:
Machine learning systems design involves creating and implementing machine learning models and algorithms to solve real-world problems.
The design process includes defining software architecture, selecting algorithms, and designing infrastructure to meet specific requirements.
The design stages include collecting and preparing data, selecting relevant features, training and validating the model, and integrating it into a broader system or application.
Monitoring and maintenance are crucial to ensure the machine learning system performs accurately and efficiently over time.
MLOps applies DevOps principles to machine learning systems to develop a software architecture capable of handling complexity and scalability, manage data and infrastructure, and automate processes for efficiency and reliability.
Machine learning systems design and MLOps are essential to ensure project success, improve model accuracy and efficiency, and deliver value to users and customers.
Challenges in Machine Learning Systems#
Machine learning systems design and development involve challenges beyond just writing the code. One of the crucial challenges is to have relevant and high-quality data. In fact, machine learning is not just about writing code; it is code plus data. Data plays a crucial role in all aspects of machine learning systems design, from selecting the right features to train the model to evaluating its performance in production.
However, working with data can also be a challenging task as data can be messy, incomplete, or biased, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of the machine learning models. Moreover, data privacy and security are also significant concerns in machine learning systems, especially when handling sensitive data such as personal information, medical records, or financial data.
Apart from the data challenges, other challenges in machine learning systems design include model selection and tuning, infrastructure and resource constraints, deployment and integration, model interpretability and transparency, and continuous improvement and maintenance. These challenges require expertise in various areas, including machine learning algorithms and models, data engineering, software engineering, and DevOps.
To overcome these challenges, it is essential to have a strong data infrastructure and governance framework in place to collect, store, and preprocess data securely and scalably. Additionally, machine learning systems design requires careful planning, design, and execution to ensure the success of the project. It involves developing effective algorithms that can learn from large amounts of data and building accurate and reliable models. Continuous monitoring, maintenance, and improvement are also necessary to ensure the models’ performance over time.
Machine learning is not just about writing code; it is code plus data.
Relevant and high-quality data is crucial to all aspects of machine learning systems design.
Data originates from a continuous and unpredictable source, often referred to as “the real world,” and is subject to constant change.
Working with the real world data can be challenging as it can be messy, incomplete, or biased.
Data privacy and security are significant concerns in machine learning systems.
Other challenges in machine learning systems design include model selection and tuning, infrastructure and resource constraints, deployment and integration, model interpretability and transparency, and continuous improvement and maintenance.
Overcoming these challenges requires expertise in various areas, including machine learning algorithms and models, data engineering, software engineering, and DevOps.
DevOps versus MLOps#
DevOps and MLOps are two related but distinct disciplines that are both focused on improving the software development and deployment process. While DevOps focuses on traditional software development, MLOps applies the same principles to machine learning.
DevOps is a methodology that combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to streamline the software development lifecycle. It involves automating the software delivery process, promoting collaboration between development and operations teams, and using tools and techniques to improve software quality and reliability.
MLOps is a similar methodology that applies DevOps principles and practices to machine learning. It focuses on the end-to-end lifecycle of machine learning models, including data collection and preparation, model training and validation, deployment and integration, monitoring and maintenance, and feedback loops for continuous improvement.
One key difference between DevOps and MLOps is the complexity of the systems involved. Traditional software development involves building applications that run on fixed inputs and provide fixed outputs. In contrast, machine learning models are highly dynamic and adaptive, making them more challenging to deploy and maintain.
MLOps requires a broader set of skills and expertise than DevOps, including machine learning algorithms and models, data engineering, statistical analysis, and more. Additionally, MLOps tools and platforms are specific to machine learning, such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Kubeflow.
Another key difference between DevOps and MLOps is the nature of the models being developed. In traditional software development, the code can be version-controlled and tested easily, while in machine learning, the models are more complex, and it’s not always easy to understand how the model arrived at its output.
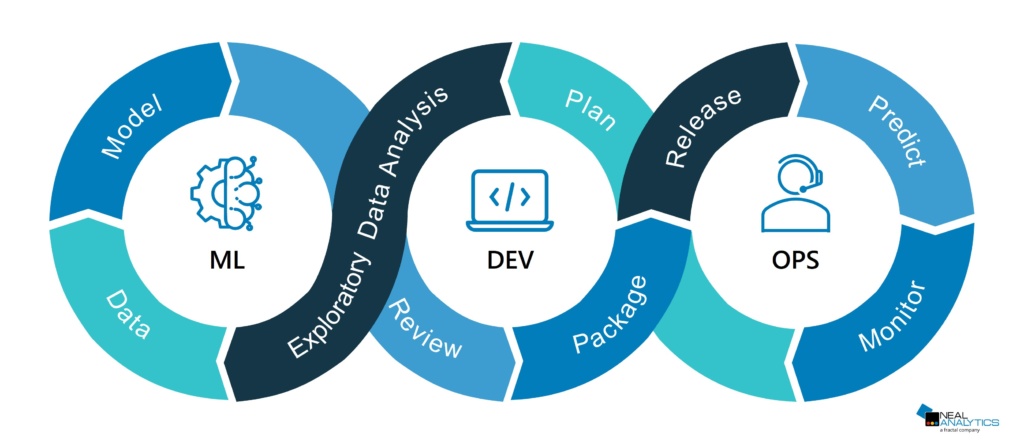
Fig. 193 The MLOps cycle. Source: NealAnalytics#
DevOps focuses on software development and IT operations, while MLOps applies the same principles to machine learning.
MLOps focuses on the end-to-end lifecycle of machine learning models, while DevOps focuses on the software development lifecycle.
MLOps involves building and deploying dynamic and adaptive machine learning models, while DevOps involves building and deploying fixed-input, fixed-output software applications.
MLOps requires a broader set of skills and expertise, including machine learning algorithms and models, data engineering, and statistical analysis, while DevOps requires expertise in software development and IT operations.
MLOps tools and platforms are specific to machine learning, such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Kubeflow, while DevOps tools and platforms are more general-purpose, such as Jenkins and Git.
Machine learning models are more complex and require different testing and maintenance strategies than traditional software applications.
MLOps involves working with more complex models that are not always easy to understand, while DevOps involves working with more straightforward applications that can be easily version-controlled and tested.
Feature |
MLOps |
DevOps |
|---|---|---|
Code |
A more comprehensive range of libraries is used as the model built to feed inferences. |
Standard libraries are used as a generic application is being made. |
Validation |
Model performance helps in the validation of the model. |
Unit, and integration testing is done. |
Roles/people involved |
1. Data scientists; |
1. Software engineers; |
Tracking/control |
Tracks hyperparameters and model performance. |
Tracks software artifacts. |
Function/development |
Delivers a machine learning model. |
A new version of the software product. |
Continuous Delivery and Automation Pipelines#
One of the key components of MLOps is the use of continuous delivery and automation pipelines to streamline the process of building and deploying machine learning models.
Continuous delivery involves automating the process of building, testing, and deploying machine learning models, allowing teams to quickly and reliably release new versions of their models into production. Automation pipelines are designed to perform a series of tasks automatically, reducing the risk of human error and improving the speed and efficiency of the process.
For example, data collection and preparation can be automated using tools like Apache Airflow or Kubeflow, which can handle tasks like data cleaning, transformation, and feature engineering. Model training and evaluation can be automated using tools like TensorFlow or PyTorch, which can perform tasks like hyperparameter tuning and model validation.
Model deployment can be automated using tools like Kubernetes or AWS SageMaker, which can handle tasks like model packaging, versioning, and scaling. Monitoring and maintenance can be automated using tools like Prometheus or Grafana, which can provide real-time metrics and alerts to ensure the model is performing as expected.
By using continuous delivery and automation pipelines in machine learning, teams can reduce the time and resources required to deploy and maintain their models, improve their accuracy and reliability, and deliver more value to their users and customers.
MLOps uses continuous delivery and automation pipelines to streamline the building and deploying of machine learning models.
Automation tools like Apache Airflow, TensorFlow, Kubernetes, and Prometheus can automate data collection, preparation, feature engineering, model training and validation, deployment, monitoring, and maintenance.
By using continuous delivery and automation pipelines, teams can reduce time and resources required to deploy and maintain models, improve accuracy and reliability, and deliver more value to users and customers.
MLOps and DevOps share similarities in continuous integration, unit testing, integration testing, and continuous delivery of software modules or packages. However, there are notable differences in ML:
Continuous Integration (CI) now includes testing and validating data, data schemas, and models, not just code and components.
Continuous Deployment (CD) involves a system (an ML training pipeline) that deploys another service (model prediction service) or rolls back changes from a model, rather than a single software package or service.
Continuous Testing (CT) is a unique property of ML systems, concerned with automatically retraining and serving the models.
Why does MLOps matter?#
MLOps is essential because machine learning projects can be challenging to implement and maintain. MLOps helps to overcome these challenges by providing a framework for managing the entire lifecycle of machine learning models, from data collection and preprocessing to model deployment and maintenance. Here are some reasons why MLOps matters:
Better collaboration: MLOps fosters collaboration between data scientists, developers, and operations teams, enabling them to work together to build and deploy machine learning models quickly and efficiently.
Faster time-to-market: MLOps enables organizations to deploy machine learning models faster and with more reliability, reducing time-to-market for new products or services.
Improved scalability: MLOps provides a scalable architecture for machine learning systems, allowing organizations to process large amounts of data and deploy models across multiple platforms and environments.
Increased accuracy and efficiency: MLOps enables organizations to monitor and fine-tune machine learning models continuously, ensuring they are accurate and efficient over time.
Reduced costs: MLOps automates many of the processes involved in developing and deploying machine learning models, reducing costs associated with manual processes and human error.
Compliance and governance: MLOps provides a framework for managing data privacy and security, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and governance policies.
How to implement MLOps#
There are various ways to implement MLOps, depending on the needs of the organization and the maturity of the machine learning process. This section provides an overview of the steps involved in implementing MLOps, as well as some best practices for each step suggested by Google.
Data science steps for ML#
The following steps can be completed manually or can be completed by an automatic pipeline.
Data extraction: You select and integrate the relevant data from various data sources for the ML task.
Data analysis: You perform exploratory data analysis (EDA) to understand the available data for building the ML model. This process leads to the following:
Understanding the data schema and characteristics that are expected by the model.
Identifying the data preparation and feature engineering that are needed for the model.
Data preparation: The data is prepared for the ML task. This preparation involves data cleaning, where you split the data into training, validation, and test sets. You also apply data transformations and feature engineering to the model that solves the target task. The output of this step are the data splits in the prepared format.
Model training: The data scientist implements different algorithms with the prepared data to train various ML models. In addition, you subject the implemented algorithms to hyperparameter tuning to get the best performing ML model. The output of this step is a trained model.
Model evaluation: The model is evaluated on a holdout test set to evaluate the model quality. The output of this step is a set of metrics to assess the quality of the model.
Model validation: The model is confirmed to be adequate for deployment—that its predictive performance is better than a certain baseline.
Model serving: The validated model is deployed to a target environment to serve predictions. This deployment can be one of the following:
Microservices with a REST API to serve online predictions.
An embedded model to an edge or mobile device.
Part of a batch prediction system.
Model monitoring: The model predictive performance is monitored to potentially invoke a new iteration in the ML process.
Implementing MLOps requires assessing the current state, defining requirements, selecting the right tools, automating the process, monitoring and maintaining, and performing continuous training and testing of the machine learning models. The level of automation of these steps defines the maturity of the MLOps process. The following are some best practices for implementing MLOps:
MLOps Level 0#
MLOps level 0 is for companies starting with ML and involves a manual, script-driven, and interactive process. It separates data scientists and engineers, has infrequent release iterations, and no CI/CD. The challenges include models breaking in the real world.
Manual, script-driven, and interactive process
Disconnect between data scientists and engineers
Infrequent release iterations
No Continuous Integration (CI) or Continuous Deployment (CD)
Deployment of a trained model as a prediction service
Lack of active performance monitoring
MLOps Level 1#
MLOps level 1 involves automating the ML pipeline to achieve continuous training of the model in production. It requires rapid experiments, CT of the model, experimental-operational symmetry, and modularized code for components and pipelines. The additional components include data and model validation, a feature store, metadata management, and ML pipeline triggers. The challenges include deploying new models based on new data instead of new ML ideas.
Rapid experiment
Continuous Training (CT) of the model in production
Experimental-operational symmetry
Modularized code for components and pipelines
Continuous delivery of models
Deployment of a whole training pipeline to serve the trained model as the prediction service
Data and model validation
Feature store
Metadata management
ML pipeline triggers
MLOps Level 2#
MLOps level 2 involves a robust automated CI/CD system and fits tech-driven companies. It includes source control, test and build services, deployment services, model registry, feature store, ML metadata store, and ML pipeline orchestrator. The characteristics include iterative ML algorithm testing and automated triggering. The challenges include manual data and model analysis steps.
Iterative testing of new ML algorithms and modeling
Automated CI/CD system
Source control
Test and build services
Deployment services
Model registry
Feature store
ML metadata store
ML pipeline orchestrator
End-to-end MLOps Solutions#
Name |
Short Description |
|---|---|
Securely govern your machine learning operations with a healthy ML lifecycle. |
|
An end-to-end enterprise-grade platform for data scientists, data engineers, DevOps, and managers to manage the entire machine learning & deep learning product life-cycle. |
|
An end-to-end machine learning platform to build and deploy AI models at scale. |
|
Platform democratizing access to data and enabling enterprises to build their own path to AI. |
|
AI platform that democratizes data science and automates the end-to-end ML at scale. |
|
An open source leader in AI with a mission to democratize AI for everyone. |
|
Automates MLOps with end-to-end machine learning pipelines, transforming AI projects into real-world business outcomes. |
|
Dedicated to making deployments of machine learning (ML) workflows on Kubernetes simple, portable, and scalable. |
|
Combines data lineage with end-to-end pipelines on Kubernetes, engineered for the enterprise. |
|
A platform for reproducible and scalable machine learning and deep learning on Kubernetes. |
|
Takes you from POC to production while managing the whole model lifecycle. |